
| Free Flag Facts | ||
| Cilck here - Animated
Flag Large Static Flag |
Cote d'Ivoire |
|
|
| Introduction | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Background:
|
Close ties to France since independence in 1960, the development of cocoa production for export, and foreign investment made Cote d'Ivoire one of the most prosperous of the tropical African states, but did not protect it from political turmoil. On 25 December 1999, a military coup - the first ever in Cote d'Ivoire's history - overthrew the government led by President Henri Konan BEDIE. Junta leader Robert GUEI held elections in late 2000, but excluded prominent opposition leader Alassane OUATTARA, blatantly rigged the polling results, and declared himself winner. Popular protest forced GUEI to step aside and brought runner-up Laurent GBAGBO into power. GBAGBO spent his first two years in office trying to consolidate power to strengthen his weak mandate, but he was unable to appease his opponents, who launched a failed coup attempt in September 2002. Rebel forces claimed the northern half of the country and in January 2003 were granted ministerial positions in a unity government. However, the central government has yet to exert control over the northern regions and tension remains high between GBAGBO and rebel leaders. Several thousand French and West African troops remain in Cote d'Ivoire to maintain peace and help implement the peace accords. |
| Geography | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Location:
|
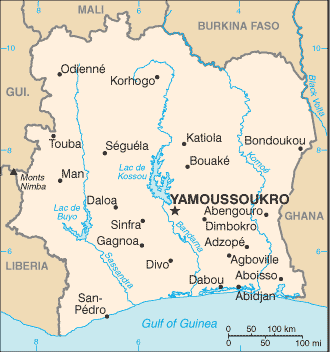
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Ghana and Liberia |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
8 00 N, 5 00 W |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 322,460 sq km
water: 4,460 sq km land: 318,000 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger than New Mexico |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 3,110 km
border countries: Burkina Faso 584 km, Ghana 668 km, Guinea 610 km, Liberia 716 km, Mali 532 km |
|
Coastline:
|
515 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
continental shelf: 200 NM
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM territorial sea: 12 NM |
|
Climate:
|
tropical along coast, semiarid in far north; three seasons - warm and dry (November to March), hot and dry (March to May), hot and wet (June to October) |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly flat to undulating plains; mountains in northwest |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Gulf of Guinea 0 m
highest point: Mont Nimba 1,752 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, natural gas, diamonds, manganese, iron ore, cobalt, bauxite, copper, hydropower |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 9.28%
permanent crops: 13.84% other: 76.88% (1998 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
730 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
coast has heavy surf and no natural harbors; during the rainy season torrential flooding is possible |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation (most of the country's forests - once the largest in West Africa - have been heavily logged); water pollution from sewage and industrial and agricultural effluents |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
most of the inhabitants live along the sandy coastal region; apart from the capital area, the forested interior is sparsely populated |
| People | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Population:
|
16,962,491
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2003 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 45.4% (male 3,796,393; female 3,902,210)
15-64 years: 52.4% (male 4,541,997; female 4,347,531) 65 years and over: 2.2% (male 179,323; female 195,037) (2003 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 17 years
male: 17.3 years female: 16.6 years (2002) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.15% (2003 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
40.01 births/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
18.41 deaths/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-0.08 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 0.97 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.92 male(s)/female total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2003 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 98.33 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 80.86 deaths/1,000 live births (2003 est.) male: 115.29 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 42.65 years
male: 40.34 years female: 45.04 years (2003 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
5.51 children born/woman (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
9.7% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
770,000 (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
75,000 (2001 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Ivorian(s)
adjective: Ivorian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Akan 42.1%, Voltaiques or Gur 17.6%, Northern Mandes 16.5%, Krous 11%, Southern Mandes 10%, other 2.8% (includes 130,000 Lebanese and 20,000 French) (1998) |
|
Religions:
|
Christian 20-30%, Muslim 35-40%, indigenous 25-40% (2001)
note: the majority of foreigners (migratory workers) are Muslim (70%) and Christian (20%) |
|
Languages:
|
French (official), 60 native dialects with Dioula the most widely spoken |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 50.9% male: 57.9% female: 43.6% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Cote d'Ivoire
conventional short form: Cote d'Ivoire local short form: Cote d'Ivoire former: Ivory Coast local long form: Republique de Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Government type:
|
republic; multiparty presidential regime established 1960 |
|
Capital:
|
Yamoussoukro; note - although Yamoussoukro has been the official capital since 1983, Abidjan remains the commercial and administrative center; the US, like other countries, maintains its Embassy in Abidjan |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
58 departments (departements, singular - departement); Abengourou, Abidjan, Aboisso, Adiake, Adzope, Agboville, Agnibilekrou, Alepe, Bocanda, Bangolo, Beoumi, Biankouma, Bondoukou, Bongouanou, Bouafle, Bouake, Bouna, Boundiali, Dabakala, Dabou, Daloa, Danane, Daoukro, Dimbokro, Divo, Duekoue, Ferkessedougou, Gagnoa, Grand-Bassam, Grand-Lahou, Guiglo, Issia, Jacqueville, Katiola, Korhogo, Lakota, Man, Mankono, Mbahiakro, Odienne, Oume, Sakassou, San-Pedro, Sassandra, Seguela, Sinfra, Soubre, Tabou, Tanda, Tiebissou, Tingrela, Tiassale, Touba, Toulepleu, Toumodi, Vavoua, Yamoussoukro, Zuenoula |
|
Independence:
|
7 August (1960) (from France) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 7 August (1960) |
|
Constitution:
|
3 November 1960; has been amended numerous times, last time 27 July 1998 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on French civil law system and customary law; judicial review in the Constitutional Chamber of the Supreme Court; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Laurent GBAGBO (since 26 October 2000); note - took power following a popular overthrow of the interim leader Gen. Robert GUEI who had claimed a dubious victory in presidential elections; Gen. GUEI himself had assumed power on 25 December 1999, following a military coup against the government of former President Henri Konan BEDIE
head of government: Prime Minister Seydou DIARRA (since 25 January 2003); note - appointed as transitional Prime Minister by President GBAGBO as part of a French brokered peace plan cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held 26 October 2000 (next to be held NA 2005); prime minister appointed by the president election results: Laurent GBAGBO elected president; percent of vote - Laurent GBAGBO 59.4%, Robert GUEI 32.7%, Francis WODIE 5.7%, other 2.2% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (225 seats; members are elected in single- and multi-district elections by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections: elections last held 10 December 2000 with by-elections on 14 January 2001 (next to be held NA 2005) note: a Senate is scheduled to be created in the next full election in 2005 election results: percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - FPI 96, PDCI-RDA 94, RDR 5, PIT 4, other 2, independents 22, vacant 2 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court or Cour Supreme consists of four chambers: Judicial Chamber for criminal cases, Audit Chamber for financial cases, Constitutional Chamber for judicial review cases, and Administrative Chamber for civil cases; there is no legal limit to the number of members |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Democratic Party of Cote d'Ivoire-African Democratic Rally or PDCI-RDA [Aime Henri Konan BEDIE]; Ivorian Popular Front or FPI [Laurent GBAGBO]; Ivorian Worker's Party or PIT [Francis WODIE]; Rally of the Republicans or RDR [Alassane OUATTARA]; Union for Democracy and Peace or UDPCI [leader NA]; over 20 smaller parties |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, AfDB, ECA, ECOWAS, Entente, FAO, FZ, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, MONUC, NAM, OAU, OIC, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Pascal Dago KOKORA
chancery: 3421 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20007 FAX: [1] (202) 462-9444 telephone: [1] (202) 797-0300 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Arlene RENDER
embassy: 5 Rue Jesse Owens, Abidjan mailing address: B. P. 1712, Abidjan 01 telephone: [225] 20 21 09 79 FAX: [225] 20 22 32 59 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal vertical bands of orange (hoist side), white, and green; similar to the flag of Ireland, which is longer and has the colors reversed - green (hoist side), white, and orange; also similar to the flag of Italy, which is green (hoist side), white, and red; design was based on the flag of France |
| Economy | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Cote d'Ivoire is among the world's largest producers and exporters of coffee, cocoa beans, and palm oil. Consequently, the economy is highly sensitive to fluctuations in international prices for these products and to weather conditions. Despite government attempts to diversify the economy, it is still largely dependent on agriculture and related activities, which engage roughly 68% of the population. After several years of lagging performance, the Ivorian economy began a comeback in 1994, due to the 50% devaluation of the CFA franc and improved prices for cocoa and coffee, growth in nontraditional primary exports such as pineapples and rubber, limited trade and banking liberalization, offshore oil and gas discoveries, and generous external financing and debt rescheduling by multilateral lenders and France. Moreover, government adherence to donor-mandated reforms led to a jump in growth to 5% annually during 1996-99. Growth was negative in 2000-02 because of the difficulty of meeting the conditions of international donors, continued low prices of key exports, and severe civil war fighting. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $24.03 billion (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
-1.6% (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $1,400 (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 29%
industry: 22% services: 49% (2001 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
37% (1995) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 3.1%
highest 10%: 28.8% (1995) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
36.7 (1995) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
3.2% (2002 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
68% agricultural (2000 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
13% in urban areas (1998) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $1.72 billion
expenditures: $2.4 billion, including capital expenditures of $420 million (2001 est.) |
|
Industries:
|
foodstuffs, beverages; wood products, oil refining, truck and bus assembly, textiles, fertilizer, building materials, electricity |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
15% (1998 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
4.605 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 61.9%
hydro: 38.1% other: 0% (2001) nuclear: 0% |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
2.983 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
1.3 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
11,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
32,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
50 million bbl (37257) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
1.35 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
1.35 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
14.87 billion cu m (37257) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
coffee, cocoa beans, bananas, palm kernels, corn, rice, manioc (tapioca), sweet potatoes, sugar, cotton, rubber; timber |
|
Exports:
|
$4.4 billion f.o.b. (2002 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
cocoa, coffee, timber, petroleum, cotton, bananas, pineapples, palm oil, fish |
|
Exports - partners:
|
France 14.5%, Netherlands 12.9%, US 7.6%, Germany 5.4%, Mali 4.6%, Belgium 4.4%, Spain 4.3% (2002) |
|
Imports:
|
$2.5 billion f.o.b. (2002 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
fuel, capital equipment, foodstuffs |
|
Imports - partners:
|
France 22.7%, Nigeria 16.6%, China 7.9%, Italy 4.2% (2002) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$10.3 billion (2002 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
ODA, $1 billion (1996 est.) |
|
Currency:
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (XOF); note - responsible authority is the Central Bank of the West African States |
|
Currency code:
|
XOF |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar - 696.99 (2002), 733.04 (2001), 711.98 (2000), 615.7 (1999), 589.95 (1998) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
263,700 (2000) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
450,000 (2000) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: well developed by African standards but operating well below capacity
domestic: open-wire lines and microwave radio relay; 90% digitalized international: satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean); 2 coaxial submarine cables (June 1999) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 2, FM 9, shortwave 3 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
2.26 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
14 (1999) |
|
Televisions:
|
1.09 million (2000) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.ci |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
5 (2001) |
|
Internet users:
|
70,000 (2002) |
| Transportation | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Railways:
|
total: 660 km
narrow gauge: 660 km 1.000-meter gauge note: an additional 622 km of this railroad extends into Burkina Faso (2002) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 50,400 km
paved: 4,889 km unpaved: 45,511 km (1999 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
980 km (navigable rivers, canals, and numerous coastal lagoons) |
|
Pipelines:
|
condensate 107 km; gas 223 km; oil 104 km (2003) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Abidjan, Aboisso, Dabou, San-Pedro |
|
Airports:
|
36 (2002) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 7
over 3,047 m: 1 2,438 to 3,047 m: 2 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 (2002) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 29
1,524 to 2,437 m: 7 914 to 1,523 m: 14 under 914 m: 8 (2002) |
| Military | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Military branches:
|
Army, Navy, Air Force, paramilitary Gendarmerie, Republican Guard (includes Presidential Guard) |
|
Military manpower - military age:
|
18 years of age (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 4,035,462 (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 2,110,276 (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 198,115 (2003 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$143.5 million (FY02) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1.4% (FY02) |
| Transnational Issues | Cote d'Ivoire |
|
Disputes - international:
|
rebel fighting extended to neighboring states and has driven out nationals and foreign workers to nearby countries; the Ivorian Government accuses Burkina Faso and Liberia of supporting Ivorian rebels |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
illicit producer of cannabis, mostly for local consumption; transshipment point for Southwest and Southeast Asian heroin to Europe and occasionally to the US, and for Latin American cocaine destined for Europe and South Africa; while rampant corruption and inadequate supervision leave the banking system vulnerable to money laundering, the lack of a developed financial system limits the country's utility as a major money-laundering center |